The alarming lack of transparency present in AI foundation models is underscored by a Stanford study.
In Brief
Stanford's team of researchers has identified a steady decline in the transparency associated with AI foundation models and are advocating for greater data disclosure from developers.
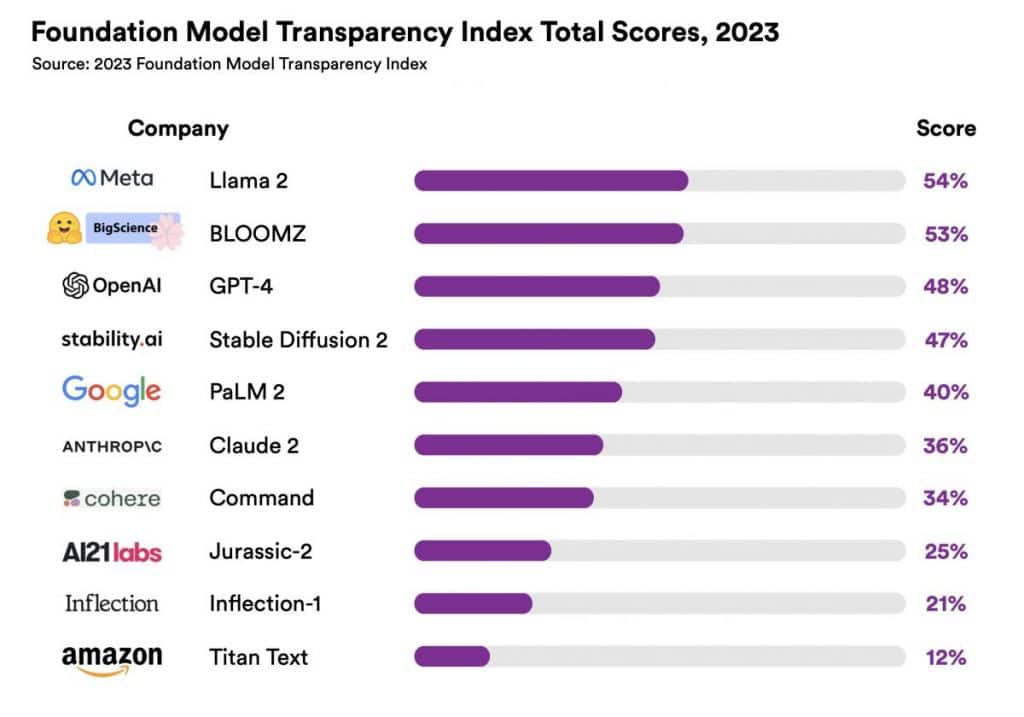
Out of the ten models evaluated, the LLaMA 2 model stood out as the most transparent with a score of 54%, while GPT-4 followed closely with 48%. In contrast, Amazon's Titan received the lowest rating at just 12%.

The researchers at Stanford University have put forward a detailed report called the Foundation Model Transparency Index, assessing models developed by companies like OpenAI and Google. unveiled This report raises significant concerns regarding the dwindling transparency of AI models. It accentuates the necessity for companies to provide insights into their data sources and the human contributions involved in training, highlighting the potential dangers that come with opacity in the AI sector.
"Over the past three years, it has become apparent that while capabilities are rapidly improving, transparency is diminishing at an alarming rate. This is concerning since we've seen in social media that a lack of transparency can lead to negative outcomes,\" explained Percy Liang, a Stanford professor involved in the Foundation Model Transparency Index.
Foundation models, which play a crucial role in advancements of generative AI and automation, received low scores in the Foundation Model Transparency Index; even the top-rated model, Meta's LLaMA 2, managed only a 54 out of 100.
The lowest score went to Amazon’s Titan model, which earned a mere 12 out of 100, while OpenAI’s GPT-4 scored 48, and Google’s PaLM 2 was rated at 40.
The authors of this report hope it sparks a movement towards improved transparency within the AI sphere and serves as a foundational resource for lawmakers confronted with the regulatory challenges posed by this rapidly evolving technology.
In the European Union, there is a push towards implementing the landmark 'Artificial Intelligence Act', which aims to develop the first all-encompassing regulatory framework for AI. This initiative intends to classify AI tools based on their risk levels while addressing issues related to biometric surveillance, the spread of false information, and biased language. Companies operating within the EU that utilize generative AI tools, such as ChatGPT, will be required to disclose any copyrighted material that was part of their development process, thereby fostering transparency.
The European Union recently made progress Please note that the information presented on this page is not intended as legal, financial, or investment advice. It is essential to invest only what you can afford to lose, and to seek independent financial counsel if you're uncertain. For detailed guidance, it's advisable to check the terms and conditions as well as the help sections provided by the issuer or advertiser. MetaversePost prioritizes accurate and unbiased reporting, yet market conditions may change without prior notice.
Disclaimer
In line with the Trust Project guidelines Agne is a journalist with a keen focus on the latest trends and developments within the metaverse, AI, and Web3 industries for Metaverse Post. Her love for storytelling has led her to conduct various interviews with industry experts, always in pursuit of engaging and inspiring narratives. Agne holds a Bachelor's degree in literature and has a wealth of experience writing about a broad spectrum of topics, including travel, culture, and the arts. Additionally, she has volunteered as an editor for an animal rights organization, where she raised awareness on issues concerning animal welfare. You can reach her at







