Smart Contracts: Transforming Industries like Supply Chain, Healthcare, and Real Estate Management
In Brief
Leveraging advanced ledger technology, smart contracts facilitate self-excuting, anonymous interactions and agreements. This innovation redefines traditional contract law for our digital world, enabling commitments and operations to be encoded in a practical manner.
The notion of smart contracts has piqued the interest of businesses, legal professionals, and tech innovators. The same ledger technology that supports cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin also enables the creation of smart contracts. These are self-executing agreements where the terms are programmed directly into code, allowing for trustworthy transactions to occur among anonymous individuals without the need for a central authority.
In 1994, Nick Szabo first introduced the concept of smart contracts. He envisioned them as a way to modernize the legal agreements we rely on today. Szabo defined a smart contract as a compilation of digital commitments alongside the processes participants must adhere to in order to fulfill those commitments.
The Smart Contract’s Development
Traditional contracts tend to be encumbered by legal jargon, which can be open to various interpretations. This can lead to conflicts that have to be resolved in courts or other mediation avenues. In contrast, smart contracts are rooted in straightforward code that operates automatically when pre-defined conditions are met.
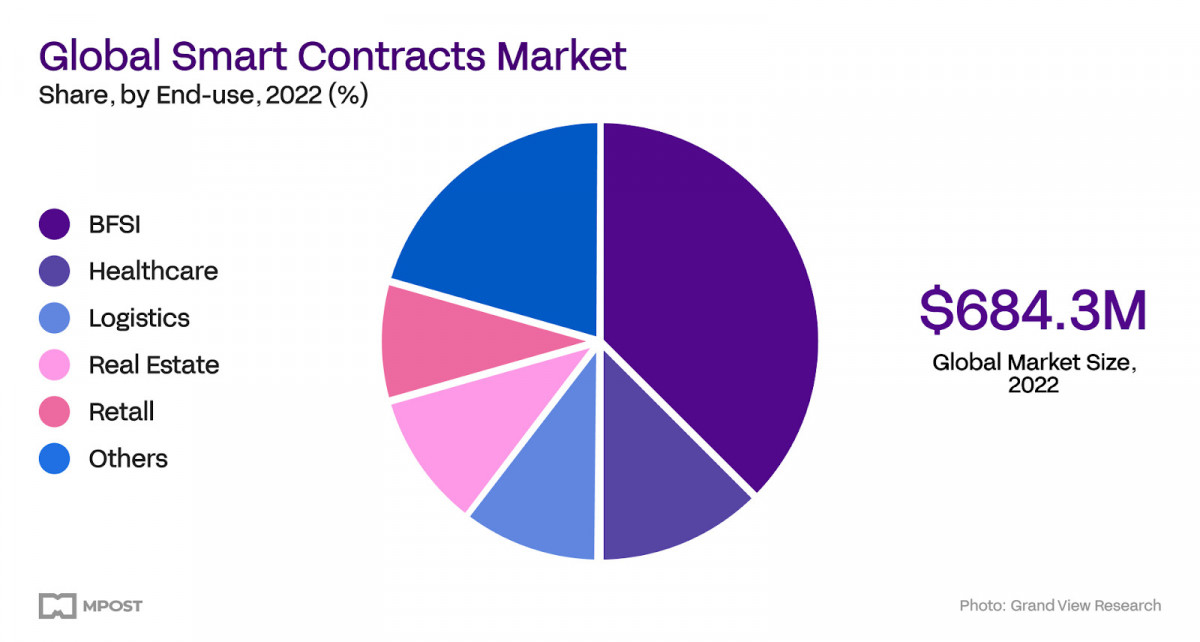
Photo: Grand View Research
One of the standout features of smart contracts is their autonomous nature. Once they are executed on a blockchain, they become immutable and unstoppable. They will perform their designated tasks without any need for intervention from the involved parties or external entities. This ensures accountability since outcomes are predetermined and transparent, with the code accessible to all stakeholders.
Exploring Smart Contract Applications Beyond Finance
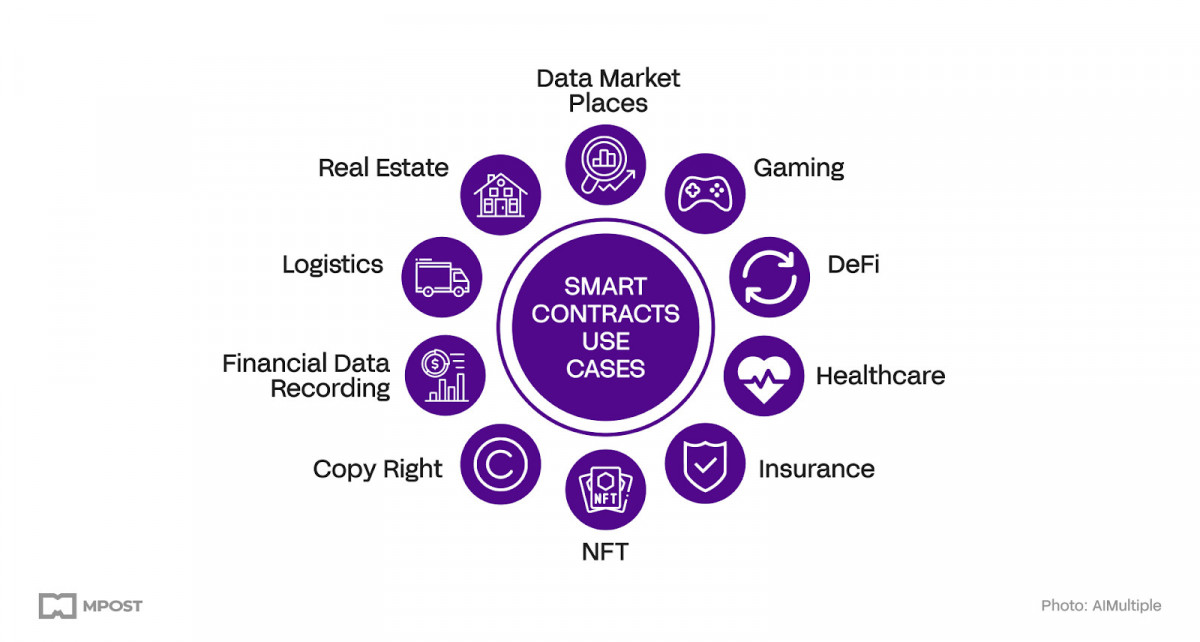
Photo: AIMultiple
Despite their initial design for financial exchanges, the potential applications of smart contract platforms stretch far beyond economics. Here are a few of the diverse areas that are currently feeling the impact of smart contracts:
Supply Chain Management
The supply chain is often bogged down by extensive documentation, complex protocols, and numerous stakeholders. Smart contracts can simplify and automate key components of supply chain management, such as tracking product movement, processing payments upon delivery, and ensuring compliance with regulations.
Healthcare
The healthcare field stands to gain significantly from smart contracts. With these technologies, electronic health records can be stored and managed securely, facilitating easy data sharing among healthcare providers while protecting patient privacy. Additionally, smart contracts could streamline clinical trial processes, manage insurance claims, and even assist in the matching and allocation of organ donations.
Real Estate
In the realm of real estate, smart contracts could revolutionize numerous processes related to property transactions, including banking services, leasing agreements, and title transfers. By utilizing smart contracts, the real estate landscape can become more efficient, accelerating transaction times and minimizing errors and disputes.
Intellectual Assets
Additionally, smart contracts can automate royalty payments to creators, paving the way for secure and transparent licensing arrangements, along with creating solid records of ownership.
The Internet of Things
With the Internet of Things (IoT) connecting billions of devices, these gadgets can share data and communicate. Smart contracts can facilitate automated interactions and transactions between these devices, opening doors for innovations in areas like industrial automation, self-driving vehicles, and smart home technologies.
Energy Exchange
Smart contracts also hold the potential for peer-to-peer energy trading, allowing individuals and organizations to buy and sell surplus energy from renewable resources such as solar panels or wind turbines.
Elections and Government
The integrity and transparency provided by blockchain and smart contracts can enhance voting and governance. By automating processes like voter registration, ballot casting, and vote tallying, they help secure elections and reduce the risk of fraud or manipulation.
These examples merely scratch the surface of what smart contracts are capable of. Looking ahead, we can expect to witness an array of groundbreaking applications emerge across diverse fields.
Originally designed for financial transactions, smart contracts have a far-reaching scope that includes a myriad of other sectors. They are set to inspire creativity, foster innovative business models, and find applications across countless industries.
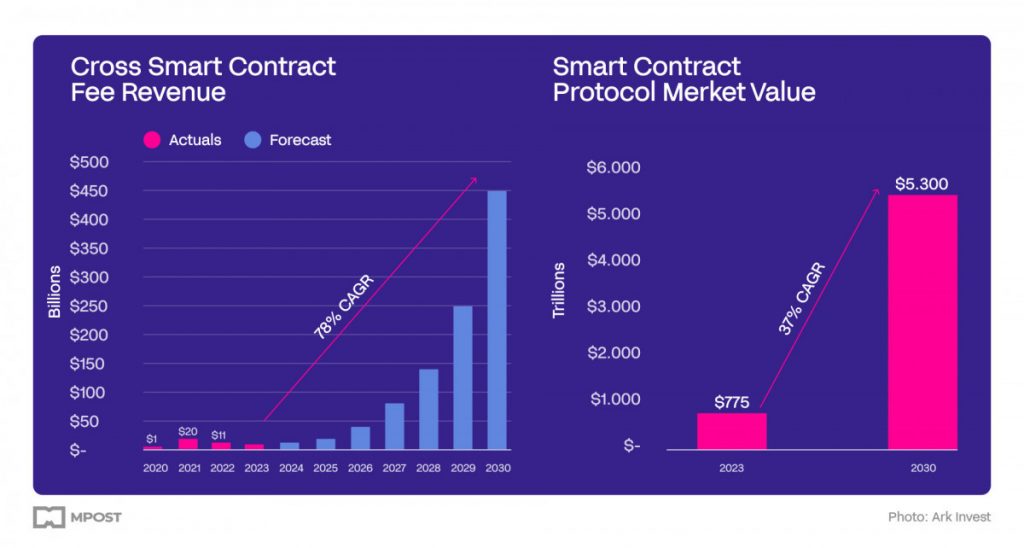
Photo: Ark Invest
Nevertheless, the successful implementation of smart contracts hinges on navigating various challenges, including security and privacy concerns, efficiency and adaptability, along with regulatory and ethical guidelines. These topics will be further explored in future articles by Metaverse Post.
Disclaimer
In line with the Trust Project guidelines Please be reminded that the information provided on this page is not to be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, or any other type of advisory. It is imperative to invest only what you can afford to lose and consider seeking independent financial advice should you have any uncertainties. For additional information, we recommend consulting the terms and conditions along with the support pages offered by the issuer or advertiser. MetaversePost is dedicated to delivering accurate and unbiased reports, but market conditions can change unexpectedly.







