Could GPT-4 Be the Game Changer for Robotics? The Revolutionary Impact of RT-2
In Brief
Google DeepMind has crafted applications from vision-language models, emphasizing their skill to generalize and share insights across various sectors. end-to-end robotic control The RT-2 model has been engineered to produce sequences that encapsulate extensive information and has undergone trials in numerous situations, such as with novel objects, different backgrounds, and diverse environmental settings.
When it comes to adapting to new scenarios, the RT-2 model surpasses some of its earlier versions, primarily due to its powerful language model.
Google DeepMind has examined how vision-language models can be utilized, particularly regarding their potential for comprehensive robotic control. Their research aimed to explore whether these models could generalize broadly. Additionally, it looked into the emergence of certain cognitive capabilities, such as reasoning and planning, which are typically linked to expansive language models.
Image Credit: Metaverse Post / Stable Diffusion The cornerstone of this investigation is deeply intertwined with the features of large language models (LLMs). Such models support any sequence that can convey an extensive array of information. This encompasses not only common linguistic constructs or programming languages like Python but also includes distinct commands.

The first number, one, indicates that the operation is still in progress and has not yet concluded. models are designed to generate The next trio of numbers, 128-91-241, represents a relative and normalized movement across three spatial dimensions. that can guide robotic actions .
The final set, 101-127-217, identifies the rotation degree of the robot's active arm section.
- to transition its state in six degrees of freedom. Consider this process akin to how humans
- retrieve overarching concepts and ideas from enormous amounts of textual information available online. The RT-2 model leverages web-based content to inform and direct robotic actions.
- The implications of this are profound. When a model is trained with a selective range of pathways that essentially indicate a specific action is needed for a desired result, it logically follows that the transformer could initiate appropriate actions based on this guidance.
Such a configuration enables the robot A vital factor being assessed was the model's ability to language models perform new tasks not included in its training regimen. This can be evaluated through several distinct methodologies:
1) Unfamiliar Objects : Can the model complete tasks when confronted with items it hasn't been trained on? Success in this area depends on its capability to translate visual input from a camera into a vector comprehensible to the language model. It should subsequently understand its significance, correlate a term with its real-world equivalent, and then instruct the robotic arm accordingly.
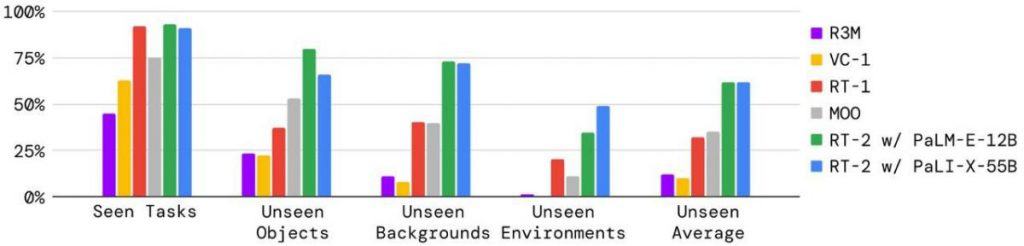
2) Different Backgrounds : How well does the model handle scenarios when most of the visual input features new elements due to an entirely different environment? For instance, if the table changes or lighting conditions shift. 3) Varied Environments : Building on the previous point, how does it perform if the entire setting is altered? To humans, these situations might appear straightforward – of course, if a person can throw a can away in their room, they should manage it outdoors, right? (On a side note, I’ve seen some folks struggle with this seemingly straightforward task in parks). But for machines, these challenges are yet to be surmounted.
Data visualizations indicate that RT-2 possesses enhanced capabilities compared to some earlier iterations, particularly when adapting to fresh conditions. This advantage largely arises from utilizing a comprehensive language model significantly bolstered by the vast array of texts it has processed during its training period.
One limitation pointed out by the researchers is the model’s struggle to adapt to entirely new skills. For example, it would fail to grasp the concept of lifting an object from its left or right unless previously encountered during training. In contrast, language models like
ChatGPT navigate this barrier with surprising ease. By analyzing massive volumes of information across various tasks, these models can quickly grasp and respond to novel requests, even if they haven’t faced them prior.
Historically, robots have functioned through a complex interplay of systems. These systems often required higher-order reasoning functions and basic manipulation components to communicate without flowing smoothly,
like a game of 'broken telephone.' Imagine trying to mentally picture an action and then having to translate that thought into your body’s movements. The fresh RT-2 model simplifies this interaction. It enables a single language model to perform advanced reasoning while simultaneously conveying commands outright to the robot. It shows that even with scarce training data, robots can perform actions they haven’t specifically been trained on.
For instance, older robotic systems needed tailored training to recognize, pick up, and dispose of waste. By comparison, RT-2 gains a basic comprehension of waste, can identify it without specific training, and can manage its disposal without prior directive on the action. Consider the intricate query, “What is considered waste?” This concept isn't straightforward to define. An empty chip bag or a banana peel transitions from being a regular item to waste after consumption. These subtle distinctions don’t require detailed explanation or extensive training; RT-2 interprets them intuitively and acts subsequently. Here’s why this technological leap is crucial and what it may mean for the future: Language models such as RT-2 operate as holistic cognitive frameworks. Their versatility in generalizing and conveying knowledge across various fields makes them supremely adaptable for diverse applications.
The researchers deliberately avoided leveraging the latest models for their experiments, aiming for each model to respond within a second (implying a robotic action rate of at least 1 Hertz). Hypothetically, employing a model like GPT-4 combined with a akin to playing a game might produce even more impressive outcomes.
While comprehensive data remains limited at this stage, the journey from the current state to a comprehensive dataset, covering everything from factory production lines to household tasks, is estimated to take approximately one to two years. This is just a rough timeline, and specialists in the area might provide more accurate projections. This surge in data is set to catalyze remarkable advancements.
Even though RT-2 was conceived using a specific approach, there are plenty of alternative methodologies to consider. The road ahead may involve a combination of these strategies, leading to further enhancements.
- One potential avenue could involve training robots utilizing videos of human actions. There’s no need for exclusive footage – platforms like TikTok and YouTube house a treasure trove of such material.
- ETH Zurich showcases robotic construction technology at CHI2022 superior visual model Meta is trialing end-to-end encryption for its Quest VR messaging platform.
- Google Unifies DeepMind and Google Brain to Accelerate AI Innovations
- Please be aware that the information presented on this page is not intended as legal, tax, investment, financial or any other kind of guidance. It's crucial to only invest what you can afford to lose and seek independent financial advice if you're unsure. For more information, we recommend checking out the terms and conditions as well as the help and support sections provided by the issuer or advertiser. MetaversePost is committed to delivering accurate and impartial reporting, although market conditions can change without notice. enhancing robotic capabilities Damir leads the team, manages products, and serves as editor at Metaverse Post, where he covers topics like AI/ML, AGI, LLMs, Metaverse, and Web3 areas. His work resonates with a vast audience, attracting over a million monthly visitors. With 10 years of experience in SEO and digital marketing, Damir’s expertise has been highlighted in publications such as Mashable, Wired, Cointelegraph, The New Yorker, Inside.com, Entrepreneur, BeInCrypto, among others. As a digital nomad, he traverses the UAE, Turkey, Russia, and the CIS. With a degree in physics, Damir believes he possesses the critical thinking capabilities essential for navigating the dynamic realm of the internet.
Read more about AI:
Disclaimer
In line with the Trust Project guidelines Solv Protocol, Fragmetric, and Zeus Network Join Forces to Introduce FragBTC: Solana's Native Yield-Generating Bitcoin Solution







