The Evolution of Zero-Knowledge Proofs: Their Journey from Cryptography to Blockchain Technologies
In Brief
Zero-knowledge proofs (ZK proofs) are cryptographic tools that allow one party to assure another that a specific assertion is true without disclosing any further details apart from the assertion's authenticity.
The concept of ZK proofs was first introduced back in 1985 by pioneering researchers Shafi Goldwasser, Silvio Micali, and Charles Rackoff.
Recently, ZK proofs have attracted significant interest for their direct integration into blockchain applications.
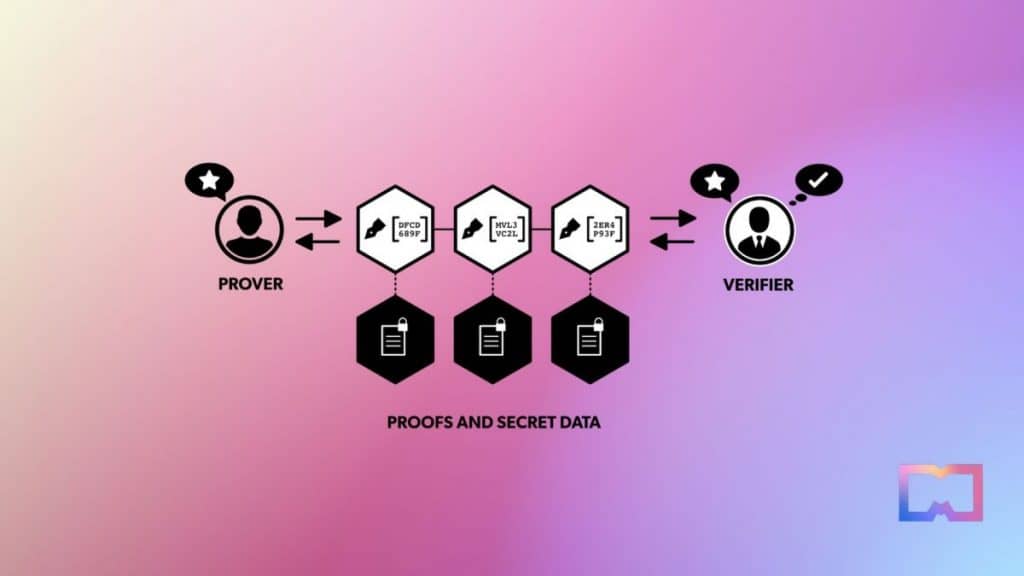
In the intricate sphere of cryptography, zero-knowledge proofs are particularly remarkable. These protocols empower a prover to convince a verifier about the truth of a claim while keeping any extra information private. The story of ZK proofs is captivating and critical across numerous domains, such as blockchain systems, privacy-focused protocols, and secure communications.

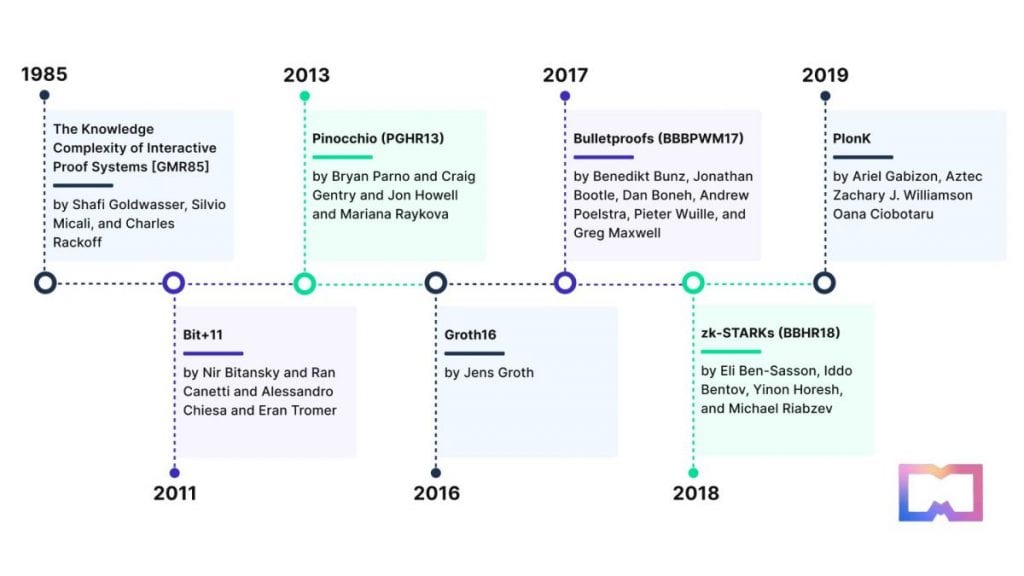
Origins in the 1980s
The foundational concept of zero-knowledge proofs was unveiled by researchers Shafi Goldwasser , Silvio Micali , and Charles Rackoff in the early 1980s. Their groundbreaking research, released in 1985, established the theoretical foundation for ZK proofs. The authors illustrated that it’s possible to craft protocols where a prover can persuade a verifier of the truth behind a statement without unveiling any information other than the statement's validity.
Three pivotal characteristics define a zero-knowledge proof: completeness (where the verifier is satisfied if the statement holds true), soundness (where the verifier is not convinced if the statement is false), and privacy (where no extra details are leaked by the prover). Achieving these three aspects together marked a significant advancement in cryptographic studies. zero knowledge A Chronological Overview of the Development of Zero-Knowledge Proofs
Application to Cryptography
Furthermore, zero-knowledge proofs have been crucial in developing digital signatures and secure identification methods. These cryptographic tools depend on the ability to prove possession of a private key without actually disclosing any details. With ZK proofs, individuals can validate their identity or assert their ownership of a key while keeping the underlying secret safe.
In more recent times, zero-knowledge proofs have garnered impressive attention, particularly regarding their relevance to blockchain technologies. The decentralized and openly transparent nature of blockchains, used by cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum, present unique challenges related to privacy and scalability. ZK proofs have emerged as a viable solution for addressing these concerns.
ZK Proofs and Their Role in Blockchain Implementation
One notable innovation is ZK-SNARKs (Zero-Knowledge Succinct Non-Interactive Argument of Knowledge), which facilitate transaction validation while concealing sensitive data. This means blockchain users can demonstrate that a transaction is legitimate without having to disclose any specifics about that transaction. This breakthrough significantly bolsters privacy, ensuring that transaction data remains confidential while preserving the integrity of the blockchain.
The practical usage of zero-knowledge proofs in blockchain has resulted in multiple real-world scenarios. For example, Zcash, a cryptocurrency that emphasizes privacy, employs ZK-SNARKs to facilitate shielded transactions, wherein the identities of the sender and receiver, as well as the transaction amount, are kept private. Likewise, other blockchain initiatives are leveraging ZK proofs to boost privacy, scalability, and operational efficiency.
However, the journey of zero-knowledge proofs has not halted with ZK-SNARKs. Ongoing research in the field continues to generate groundbreaking innovations. New zero-knowledge systems, including ZK-STARKs (Zero-Knowledge Scalable Transparent Arguments of Knowledge), are focusing on overcoming efficiency limitations and modifying trust assumptions present in earlier versions.
Continued Advancements
Moreover, zero-knowledge proofs are being explored beyond the boundaries of cryptography and blockchain. Their potential is being investigated in areas such as secure voting frameworks, safe cloud computing, and privacy-protected machine learning. The capacity to offer mathematical assurances while keeping sensitive information private makes zero-knowledge proofs an exceptionally potent instrument for safeguarding privacy and fostering secure exchanges across various sectors.
The narrative of zero-knowledge proofs showcases the impressive evolution of cryptography itself. From their theoretical inception in the 1980s to widespread practical applications in blockchain and other fields, ZK proofs have transformed our approach to privacy, security, and trust in the digital landscape.
Conclusion
As researchers and tech innovators continue to advance the boundaries of zero-knowledge proofs, we can look forward to even more creative applications and refined protocols. The ongoing progress within this domain promises to influence the future of secure communications, privacy considerations, and decentralized technologies, ensuring individuals can share information and conduct transactions while maintaining confidentiality and fostering trust in digital interactions.
An Introductory Overview of the zkSync Ecosystem
Read more:
- ZK-Proofs: What Advantages Do They Bring?
- ZK-Proofs: What Is Zero Knowledge?
- , bear in mind that the content on this page is not intended to be taken as, nor should it be regarded as, legal, tax, investment, financial, or any other type of advice. It is crucial to invest only what you can afford to lose and to seek independent financial counsel if you have any uncertainties. For additional details, we recommend reviewing the terms and conditions alongside the help and support resources provided by the issuer or advertiser. MetaversePost is dedicated to delivering accurate and impartial reporting, although market circumstances can change without prior notice.
vi
vi Search Nik is a skilled analyst and writer at Metaverse Post, focusing on providing cutting-edge insights into the dynamic realm of technology, particularly in areas such as AI/ML, XR, VR, on-chain analytics, and blockchain advancements. His work engages a wide audience, enabling them to stay ahead in the fast-evolving tech landscape. Holding a Master’s degree in Economics and Management, Nik possesses a thorough understanding of the intricacies within the business world and its convergence with emerging technologies.


