BEVM Introduces Innovative Taproot Consensus for a Decentralized Bitcoin Layer 2 Framework
Cardiff, UK, May 26th, 2024, Chainwire
On May 20, 2024, the development team for Bitcoin Layer 2 BEVM released a comprehensive technical paper titled \"Taproot Consensus: A Decentralized BTC Layer 2 Approach.\" This document outlines how Taproot Consensus is implemented, utilizing foundational Bitcoin technologies like Schnorr signatures, MAST, and Bitcoin SPV nodes to create a fully decentralized BTC Layer 2 solution. Taproot Consensus marks a pivotal advancement in scaling native Bitcoin, creatively employing existing Bitcoin technologies without altering the fundamental codebase.
I. Evolution of Bitcoin’s Technical Developments
- October 31, 2008: Satoshi Nakamoto released \"Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System,\" laying the groundwork for Bitcoin and introducing Simple Payment Verification (SPV).
- January 3, 2009: Nakamoto successfully mined the Genesis Block, officially launching Bitcoin. Initially, the code employed ECDSA for digital signatures rather than the more suitable Schnorr signatures, which were still under patent. Schnorr signatures not only maintain the security features of ECDSA but also excel beyond the 15-signature cap of ECDSA, allowing for Bitcoin management across thousands of addresses without compromising signing speed.
- 2018: Core developers within the Bitcoin community proposed the integration of Schnorr signatures into the Bitcoin network.
- November 14, 2021: The Taproot upgrade brought forward Schnorr signatures along with MAST (Merkelized Abstract Syntax Trees), enhancing capabilities for smart contracts and decentralized multi-signature management.
- BEVM's Taproot Consensus builds upon these enhancements, merging Schnorr signatures and MAST to effectively handle multi-signature addresses, facilitating complex business applications in Bitcoin Layer 2.
II. Summary of the Taproot Consensus Framework:
The yellow paper starts by emphasizing Bitcoin’s limitations regarding Turing-completeness and its constrained functionalities for smart contracts. It proposes that instead of altering Bitcoin Layer 1, we should leverage the existing Bitcoin capabilities to develop a decentralized Layer 2 solution.
BEVM’s Taproot Consensus ingeniously combines the advancements of Bitcoin’s Taproot technology, which includes Schnorr signatures and MAST, Bitcoin SPV light nodes, alongside a Byzantine Fault Tolerant (BFT) Proof of Stake (PoS) consensus mechanism, establishing a coherent and decentralized Layer 2 network.
III. In-depth Analysis of Taproot Consensus Structure
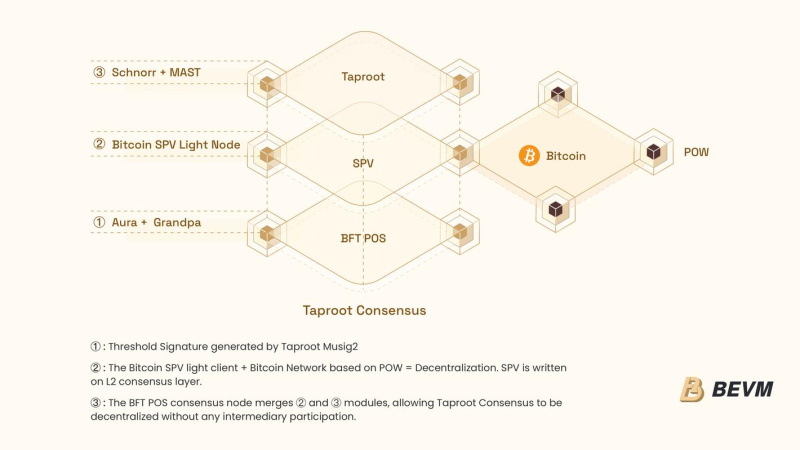
The architecture of Taproot Consensus consists of three key elements: Schnorr+MAST, Bitcoin SPV, and Aura+Grandpa.
· Schnorr+MAST: Utilizes these technologies from the Taproot upgrade to facilitate decentralized management of Bitcoin multi-signatures, all governed by Bitcoin’s code.
· Bitcoin SPV: Enables synchronization and validation of Bitcoin transactions without the necessity of operating a complete node.
· Aura + Grandpa: Sophisticated PoS consensus protocols that provide Byzantine fault tolerance, maintaining high consistency among nodes within the network.
In the BEVM framework, each validator is entrusted with a BTC private key for Schnorr signatures. The collective public key constructs a MAST tree, which allows for BTC transactions and inscriptions directed to a threshold signature address. Validators serve as Bitcoin SPV light nodes, ensuring the synchronization of the BTC network state in a secure and permissionless manner. Aura+Grandpa underscores the security and reliability of the Layer 2 network, with asset management governed by a BFT consensus mechanism.
The operational method of Taproot Consensus follows this principle: \"Within the BEVM system, validators maintain a BTC private key for Schnorr signatures. The inherent features of Schnorr signatures facilitate effective signature aggregation, which in turn bolsters both security and efficiency of the system. The aggregated public key, Pagg, is produced through the Musig2 multi-signature scheme and creates an extensive MAST (Merkle Abstract Syntax Tree). After the root hash of the MAST tree is established, validators can execute BTC transactions and inscriptions to the threshold signature address designed by the MAST tree, allowing data to flow from the Bitcoin mainnet to the BEVM network. Furthermore, each validator acts as a light node using Bitcoin SPV, which permits the safe and unrestricted synchronization of the BTC network state.\"
IV. Additional Technical Insights from the Yellow Paper – Achieving True Decentralization
The yellow paper also delves into the application of Schnorr signatures, MAST, Bitcoin SPV light nodes, and the Aura+Grandpa consensus mechanisms, offering a thorough technical overview catering to those keen on Bitcoin technologies. It elucidates the Musig2 implementation while drawing comparisons with other BTC Layer 2 projects such as Mezo that utilize the tBTC protocol. Contrarily to tBTC, which depends on a network of nine signers, Taproot Consensus harmonizes multi-signature networks with BFT PoS consensus, attaining genuine decentralization.
Moreover, the yellow paper outlines the Musig2 implementation process and distinguishes between various BTC Layer 2 initiatives like Mezo and Taproot Consensus. Mezo bases its technical foundation on the tBTC protocol, which constructs a threshold signature network using Bitcoin multi-signatures, offering strong cohesion compared to conventional distributed systems. Nevertheless, tBTC’s reliance on a nine-signatory framework contrasts with the pursuit of a genuinely decentralized system, which should derive consensus from the integration of multi-signature networks and BFT PoS mechanisms. This distinction elucidates the difference between distributed frameworks and blockchains; while distributed networks prioritize distribution, they often lack Byzantine fault-tolerant consensus, whereas blockchains, despite being distributed networks, operate on Byzantine fault-tolerant consensus, achieving true decentralization. The Taproot Consensus model employs this sophisticated design. By unifying Schnorr signatures, MAST, Bitcoin SPV light nodes, and the Aura and Grandpa mechanisms for Byzantine fault tolerance, it creates a robust decentralized Layer 2 scalability solution. This cohesive structure not only improves the scalability and overall usability of the Bitcoin platform but also ensures the security and integrity of the BEVM network.
Conclusion
The comprehensive technical yellow paper put forth by the BEVM team meticulously outlines Taproot Consensus, a BTC Layer 2 framework constructed entirely on inherent Bitcoin technologies. It honors and innovates upon Bitcoin’s foundational technical trajectory, positioning itself as a true advancement in native Bitcoin scalability solutions. As the Bitcoin landscape continues to evolve, frameworks like Taproot Consensus are bound to play a pivotal role, serving as essential elements for the genuine advancement of decentralized Bitcoin Layer 2 solutions.
About BEVM
BEVM stands out as the first fully decentralized Bitcoin Layer 2 solution that is compatible with Ethereum’s EVM. It empowers DApps within the Ethereum realm to function seamlessly on the Bitcoin network, utilizing BTC as gas. BEVM significantly enhances Bitcoin’s versatility by creating a secure and scalable foundation for decentralized applications. This system integrates advanced consensus frameworks, inter-chain interactions, and robust data integrity measures, promising a fluid user experience. BEVM aims to drive innovation within the Bitcoin environment, offering enhanced scalability, security, and compatibility with widely-used Ethereum tools and applications.
For further insights, users are encouraged to visit BEVm’s official website or follow BEVM on Twitter .
Contact
Tommie
BEVM
Disclaimer
In line with the Trust Project guidelines , however, please be aware that the content available on this page is neither designed to serve as nor should be interpreted as legal, tax, investment, financial, or any other type of advice. It remains crucial to only invest what you can afford to lose and consult with independent financial advisors should you have any uncertainties. For additional guidance, we recommend checking the terms and conditions, along with the help and support sections made available by the issuer or advertiser. MetaversePost commits itself to delivering precise and unbiased reporting, although market conditions may evolve without prior notice.







