The MinD-Vis model demonstrates a fascinating ability to grasp what a person is perceiving, simply by examining their brain activity.
In Brief
This AI model has the ability to analyze and make sense of what a person observes through their sight. brain activity – here’s how
The MinD-Vis model is a groundbreaking AI tool capable of interpreting visual experiences by examining the brain's activity patterns. It focuses on decoding 'mnemonic invariants', which are essentially the consistent patterns tied to specific objects within our memories.

To achieve a global understanding of brain activity, researchers first developed a self-supervised model applicable across individuals. They subsequently implemented cross-attention techniques to enhance the mental imagery derived from the pre-existing data. Latent Diffusion Through rapid fine-tuning with a dataset of 1,500 pairs of images and fMRI scans, the model successfully interprets what an individual is actually visualizing at any given moment! fMRI pairs!
By exploring the intricacies of the human visual system, the efforts aim to broaden our comprehension of visual perception and create a link between human eye processes and computer vision via Brain-Computer Interfaces. The challenge arises from the intricate nature of brain signal representations and the scarcity of annotated data, making it tough to generate high-quality images from these signals.
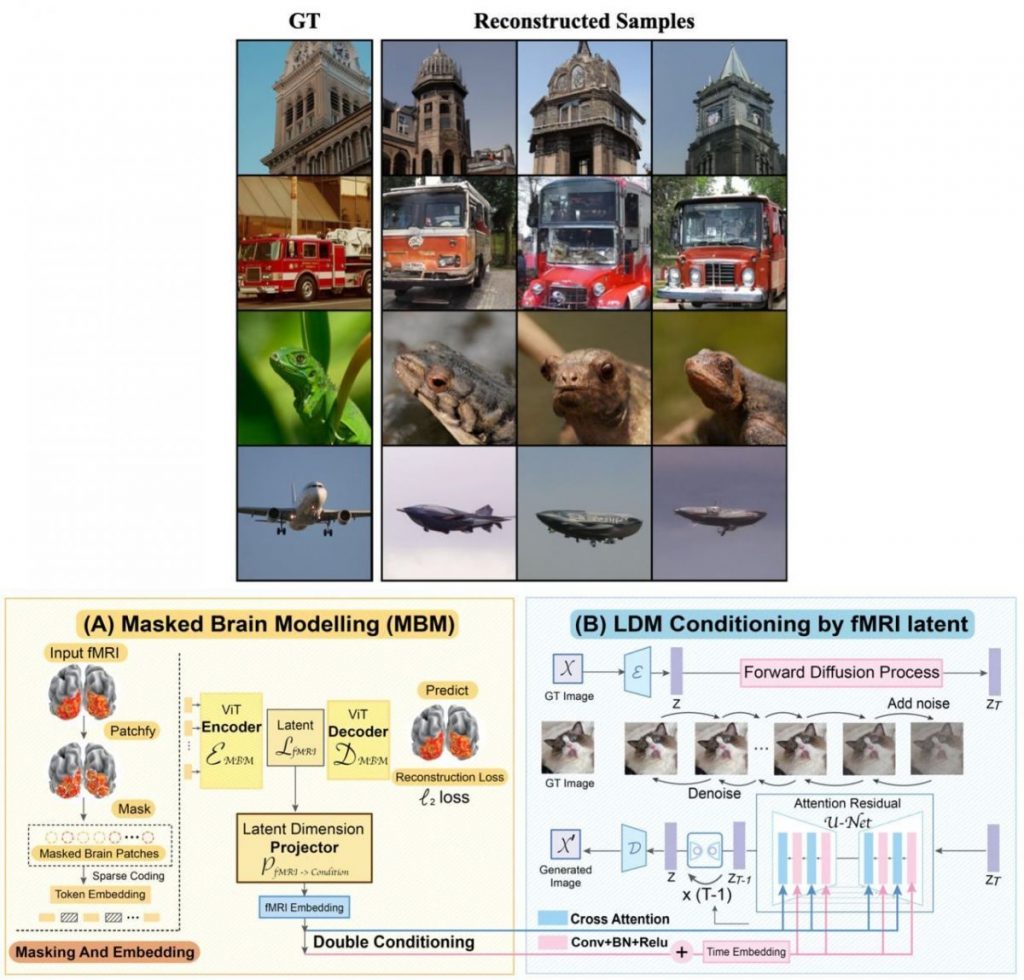
Initially, we implement mask modeling within a vast latent space, influenced by the sparse coding method used in the primary visual cortex, to form a self-supervised depiction of fMRI data. Following that, by incorporating double-conditioning into a latent diffusion framework, we demonstrate that MinD-Vis is capable of reconstructing highly authentic images with semantically relevant details derived from brain recordings, even with a limited number of paired samples.
Researchers claimed
Based on the experimental findings, this approach significantly surpassed existing benchmarks in both semantic mapping (achieving a remarkable 66% improvement in a hundred-way classification task) and image generation quality (with a 41% boost in FID scores). The model has undergone extensive qualitative and quantitative evaluations. A thorough ablation study was also performed to validate the framework.
The training datasets, code, and model weights have been made publicly accessible on various platforms. request .
The team behind the research envisions that this AI model could pave the way for developing assistive devices for individuals who are blind or visually impaired. Additionally, it holds potential applications in aiding those suffering from memory-related conditions, such as Alzheimer’s.
Read more:
Disclaimer
In line with the Trust Project guidelines Please keep in mind that the information presented on this page is not meant to be interpreted as legal, tax, investment, financial advice, or any other form of professional counsel. It’s crucial to invest only what you can comfortably afford to lose and seek independent financial guidance if you're uncertain. For more thorough insights, we recommend reviewing the issuer's or advertiser’s terms, along with the support and help sections. MetaversePost strives to deliver accurate and impartial reporting, but please be aware that market conditions can change without prior notice.







